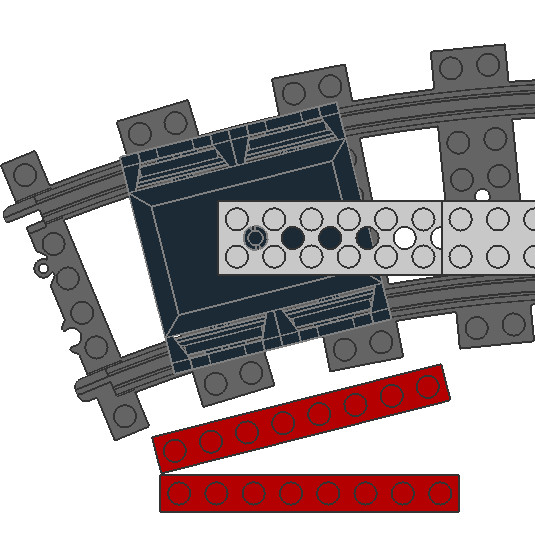
LEGO: Train bogies
Preamble
This article documents my investigation into how LEGO trains interact with curved tracks. Specifically, the relationship between bogie distance, bogie size, and the bogies' pivot radius.
"LDU" below refers to LDraw Units, where 1 LDU ≈ 0.4mm.
We start with bogies with three bogie sizes:

Track sections
Just for reference. Only curved track is in scope for now. Curved tracks represent the tightest radius that a LEGO train would be expected to travel on.
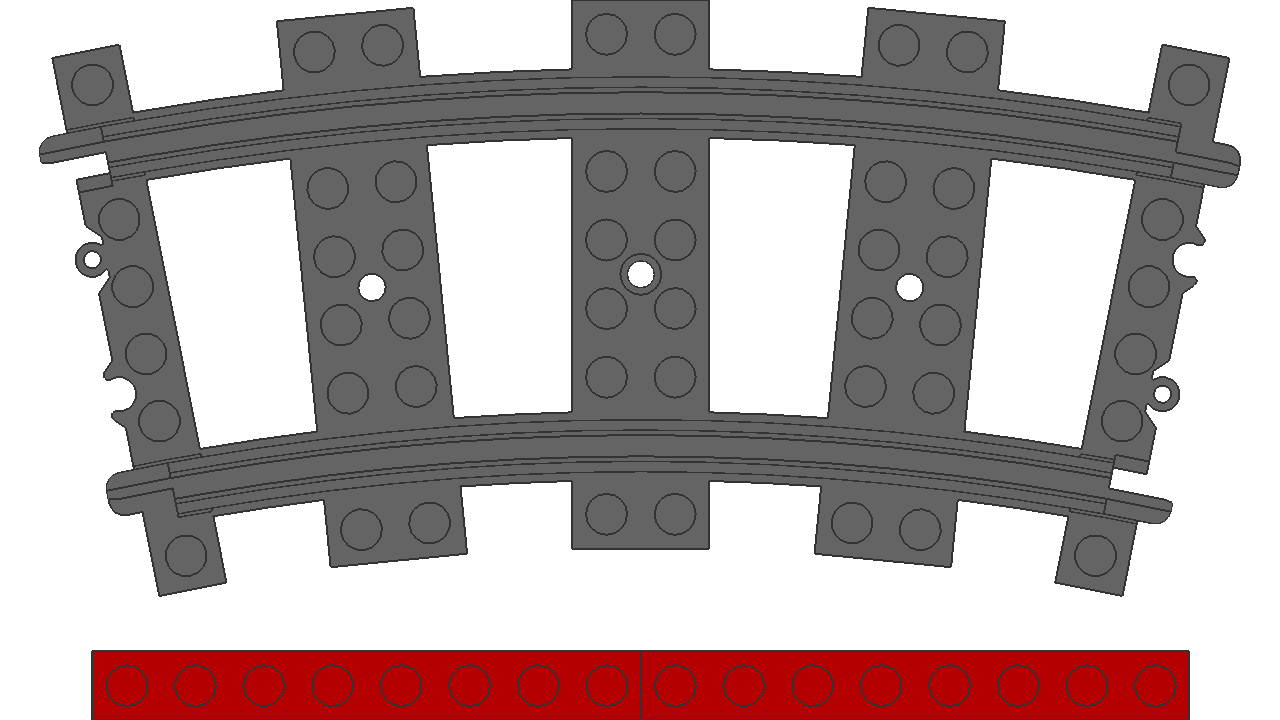
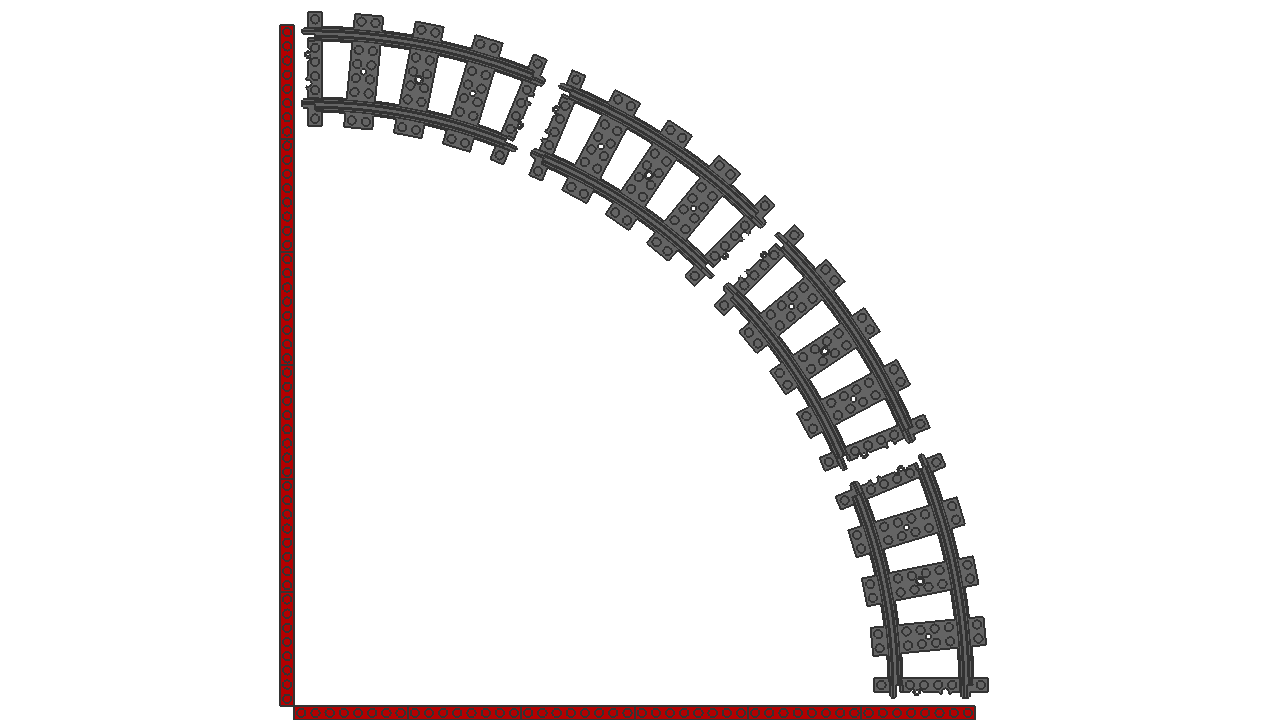
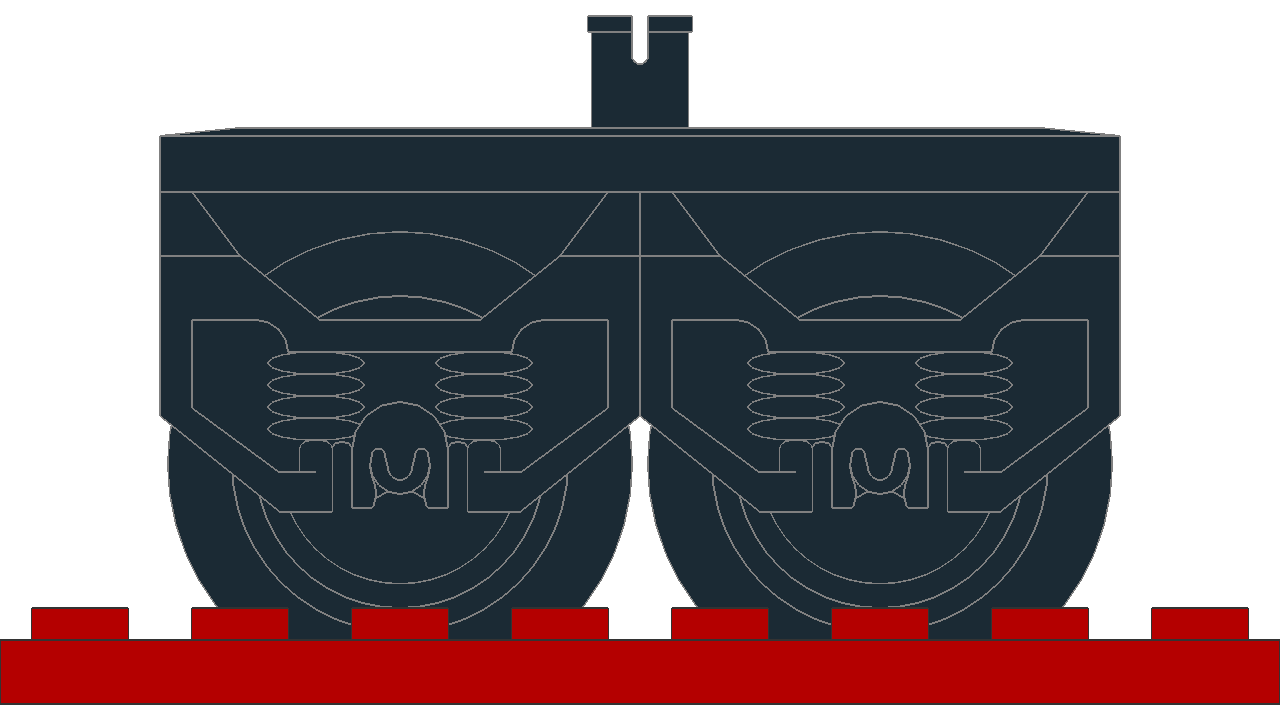
Bogies on a curved track
At the same distance, they all seem to have the same rotation from their origin. In this experiment, different sized bogies are positioned with their pivot point 400 LDU apart, fit onto the track while rotated 14.2° from their origin.
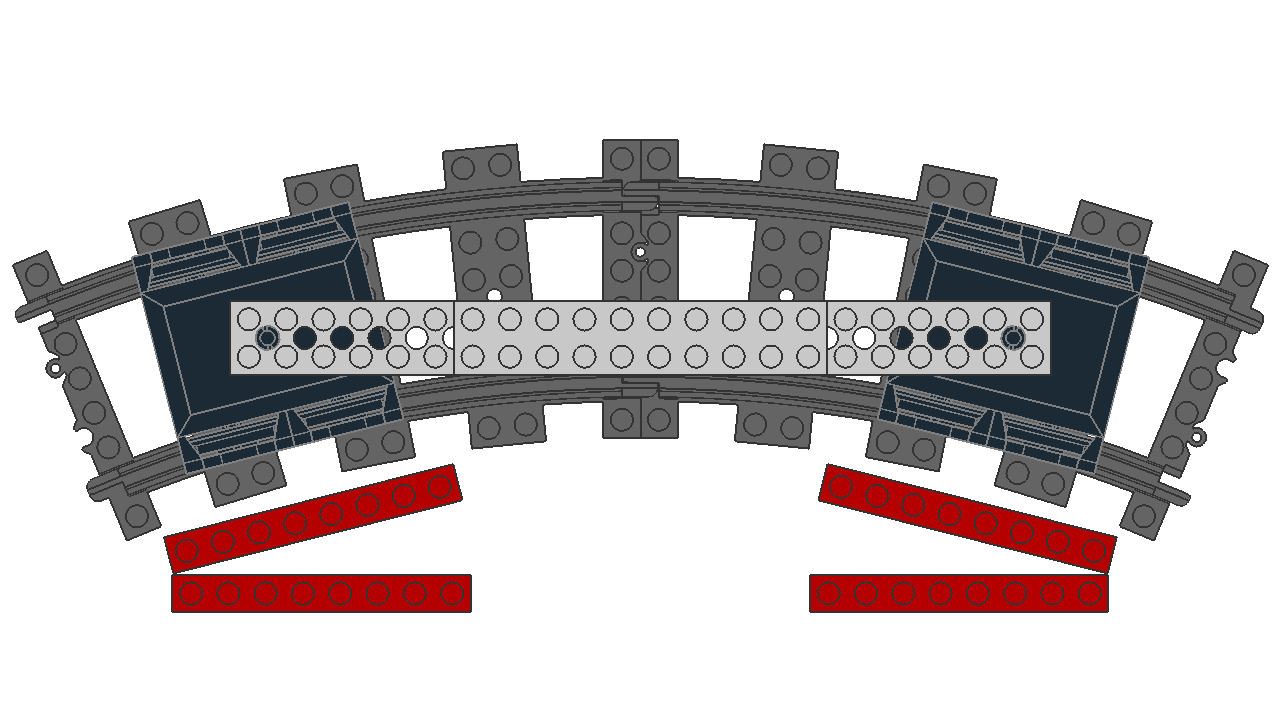
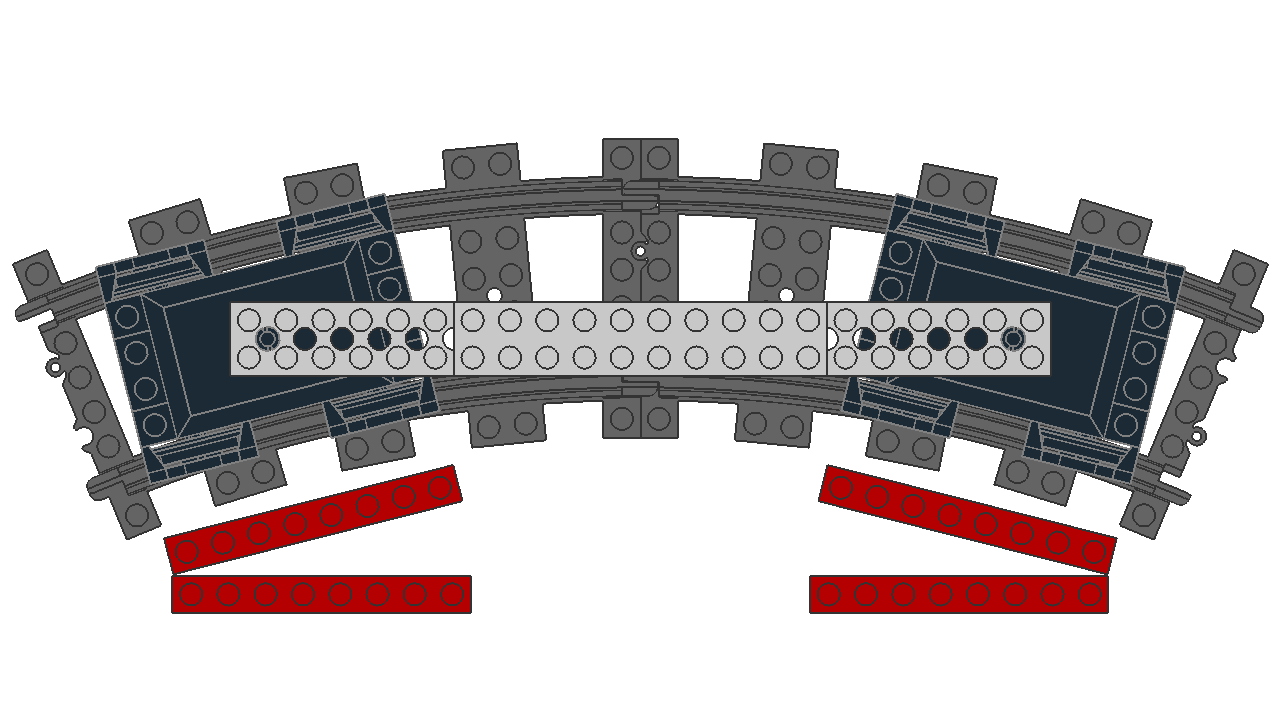
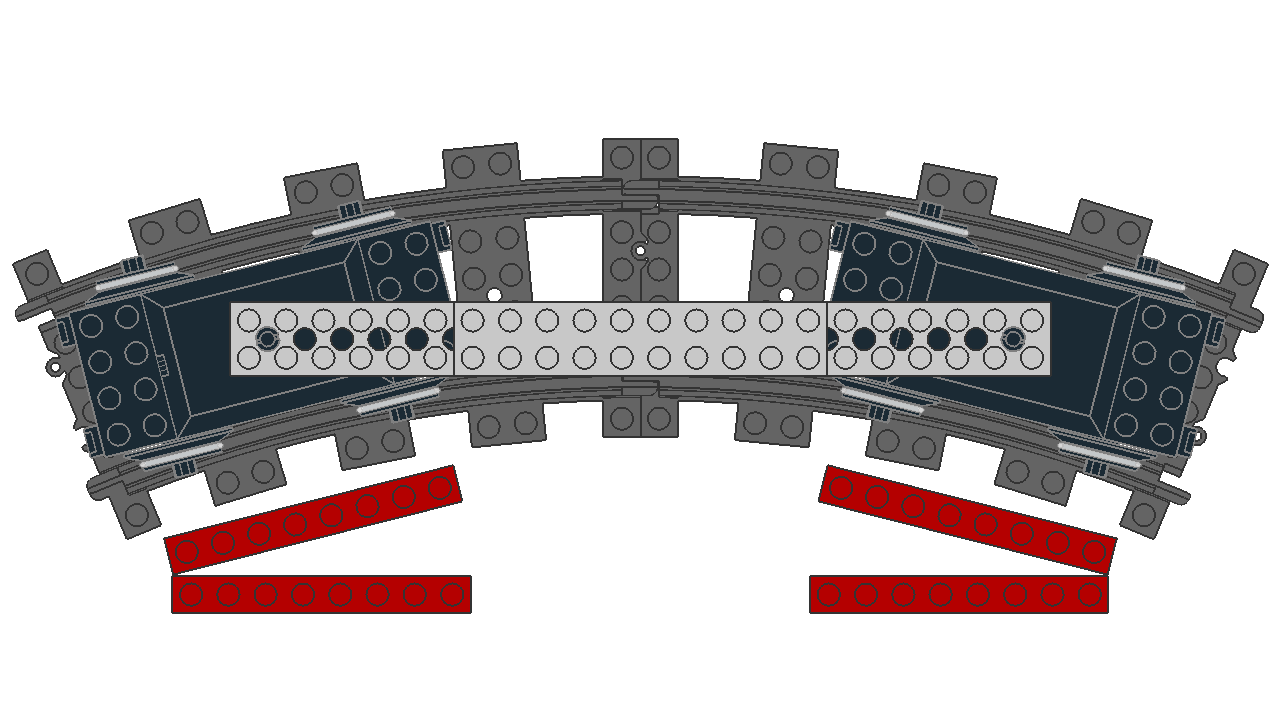
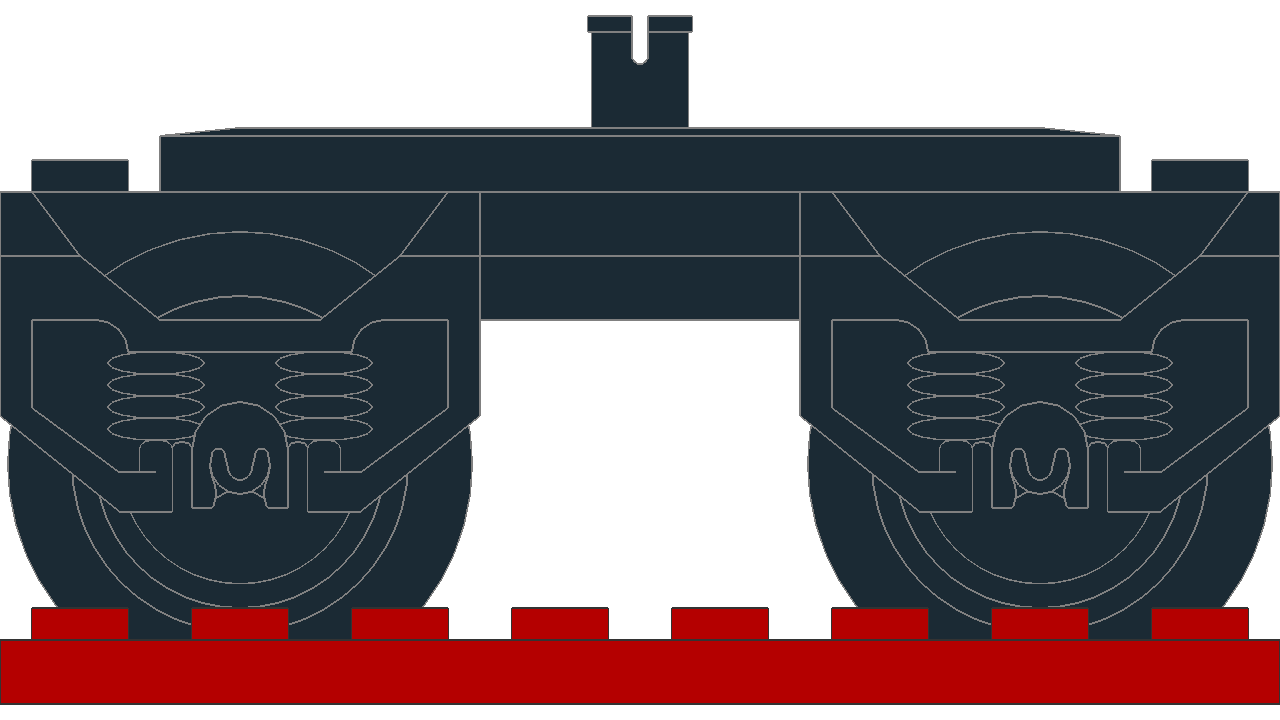
Different size trailers
At different distances, they have different rotations from their origin. In this experiment, identical 60 LDU bogies are positioned with their pivot points at different distances, which affects the rotation from their origin.
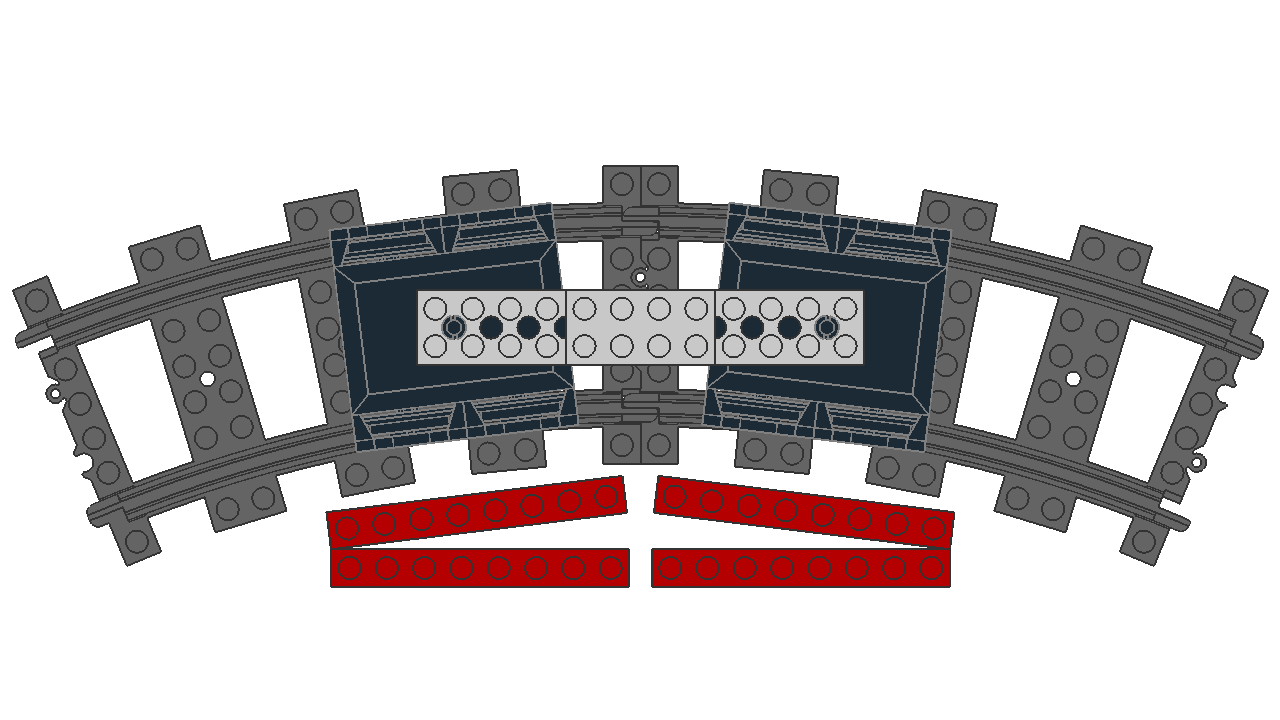

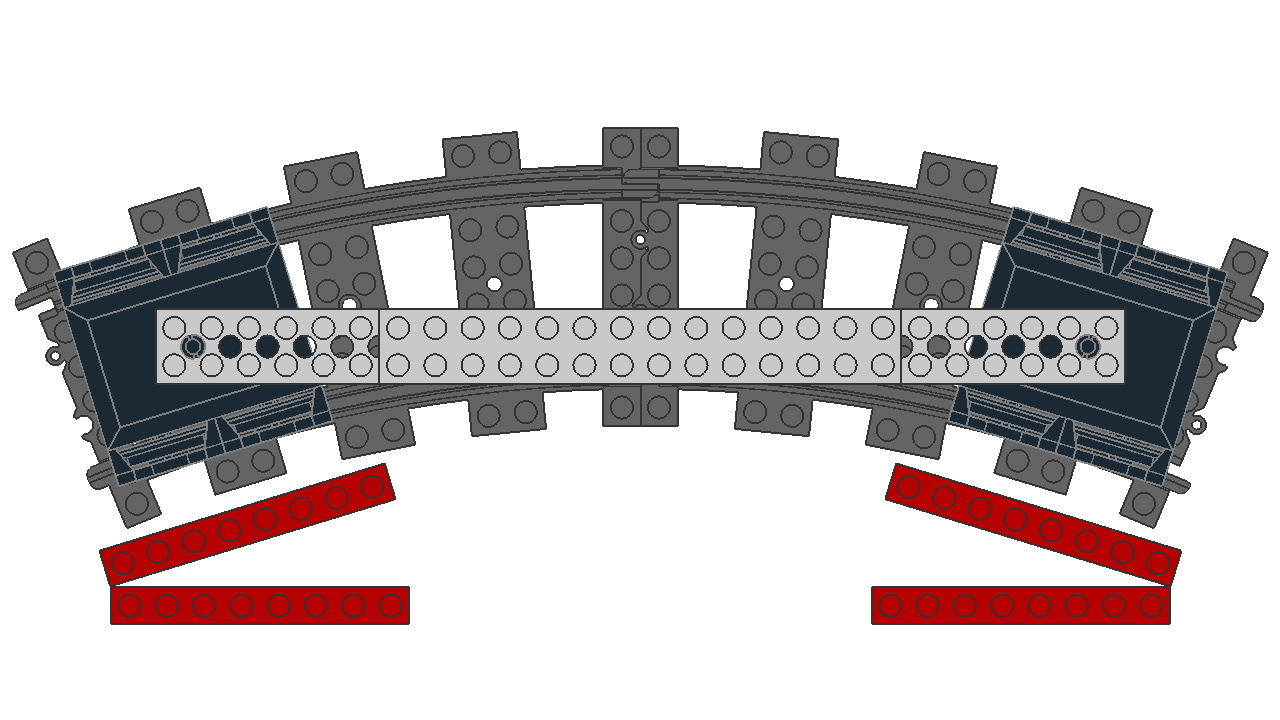
With these datapoints, we can approximate the relationship as ,
where is the pivot point distance in LDUs, and is
the bogie rotation. We can use this to evaluate different
 LEGO: Train bases.
LEGO: Train bases.
This article is part of the  LEGO set.
If you have feedback or questions about this article, let's catch up via
Mastodon or email.
LEGO set.
If you have feedback or questions about this article, let's catch up via
Mastodon or email.
;fill-rule:nonzero;stroke:%23000;stroke-width:48.7px;'/%3e%3cdefs%3e%3clinearGradient%20id='_Linear1'%20x1='0'%20y1='0'%20x2='1'%20y2='0'%20gradientUnits='userSpaceOnUse'%20gradientTransform='matrix(2406.25,-2101.13,2101.13,2406.25,1086.43,2157.14)'%3e%3cstop%20offset='0'%20style='stop-color:%232d1f30;stop-opacity:1'/%3e%3cstop%20offset='1'%20style='stop-color:%239f5060;stop-opacity:1'/%3e%3c/linearGradient%3e%3c/defs%3e%3c/svg%3e)

 All articles
All articles About Sinclair Studios
About Sinclair Studios